A computer program accepts inputs, processes it and produces the output and so in this very simple program, we accept two numbers from a user and print their sum on the screen.
Purpose
Write a program to accept two integers from a user and print their sum.
// C++ Program to add two numbers
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int num1, num2;
cout << "Enter the first number : ";
cin >> num1;
cout << "Enter the second number : ";
cin >> num2;
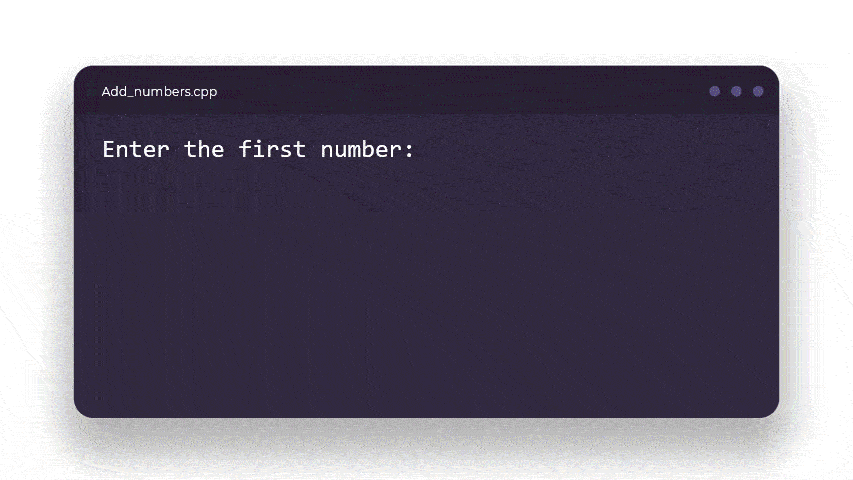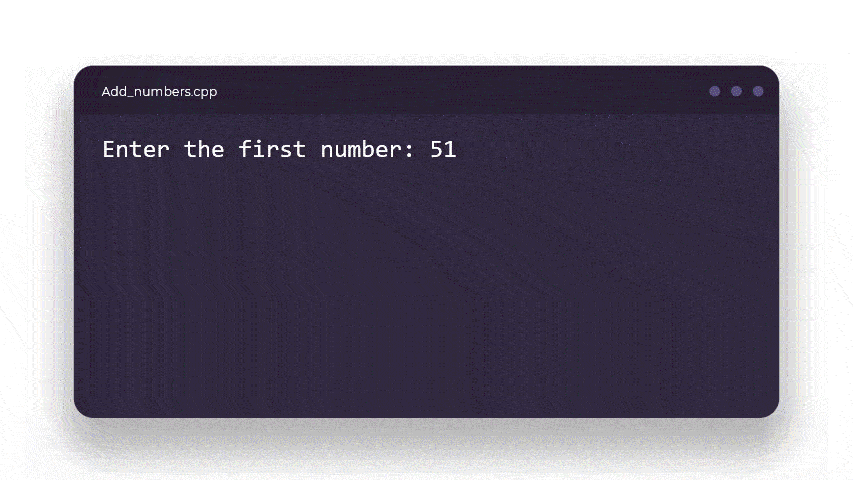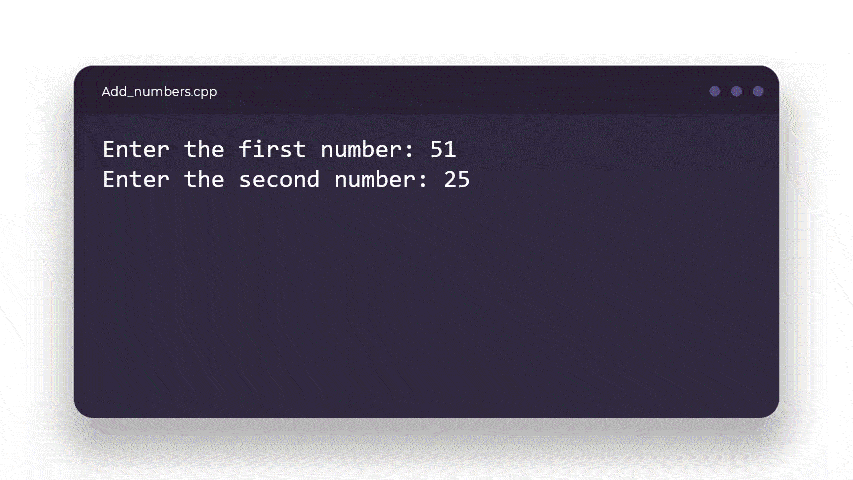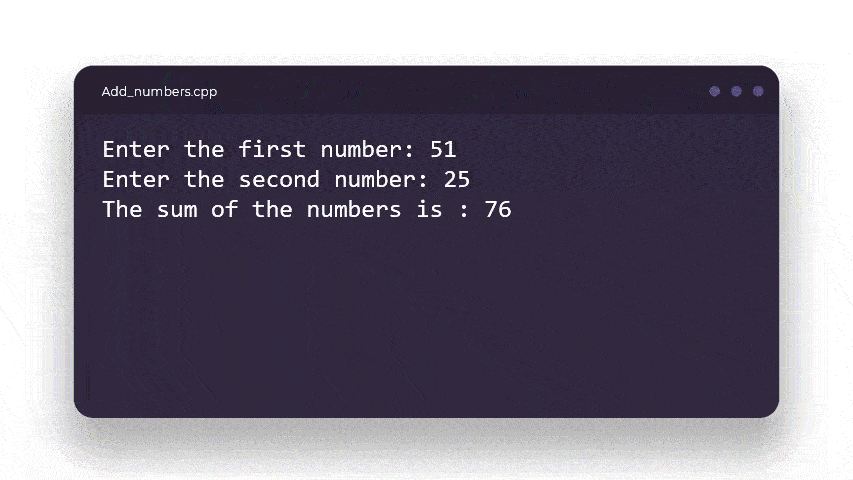
cout << "The sum of the numbers is : " << num1 + num2;
return 0;
}Alternative Way
The same program can be written without using the cout, cin but you'd have to use the stdio.h header file.
// Program to accept two numbers and print their sum
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int num1, num2, sum;
// Display request for first number
printf("Enter the first number : ");
scanf("%d", &num1); // Get first number and store it in num1 variable
// Display request for second number
printf("Enter the second number : ");
scanf("%d", &num2); // Get second number and store it in num2 variable
// Add the two numbers
sum = num1 + num2;
// Print the sum of the numbers
printf("Sum of two numbers = %d", sum);
return 0;
}Explanation
The program accepts two numbers from a suer and adds the two numbers and prints their sum on the screen. As you can see in the sample code above, the program requires iostream header file. This header file contains the definition of cout and cin constructs.
The program then starts from the main() function. The first thing it encounters is the Integer variable declaration to store the user input. The programt then prints the message to the user requesting input for the first number. After entering the first number the user presses the enter key and request for second number is made.
The program then finally prints the sum of the two numbers to the user. This is a very basic program one learns when starting coding with C or C++.